The vertebrates include over 45,000 living species. Vertebrates range in size from tiny fish to elephants and whales (weighing up to 100 tonnes), the largest animals ever known. Vertebrates are creatures that have adapted to live underground, above ground, and both. They consume invertebrates, plants, and occasionally one another. Names for vertebrates that are frequently used include whale, lion, bat, owl, elephant, frog, etc.
What are Vertebrates?
Vertebrates are a chordate group that comprises birds, mammals, fishes, lampreys, amphibians, and reptiles. Vertebrates have a vertebral column, which replaces the notochord with numerous vertebrae that create a backbone. The vertebrae give the animal structural support in addition to encircling and shielding the nerve cord.
Vertebrates have two sense organs, a unique brain enclosed in a skull, and an evolved head. They also have a highly effective respiratory system, a muscularized gut, a chambered heart, and a throat with slits and gills (though these structures are significantly altered in terrestrial vertebrates).
Classification of Vertebrates
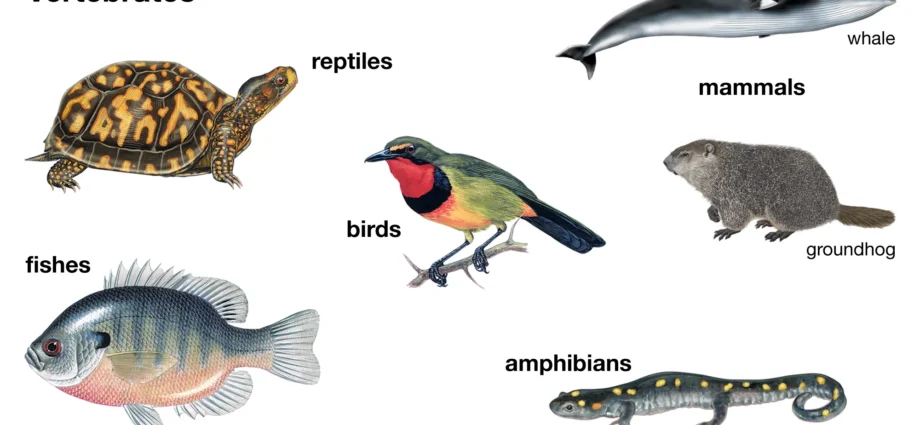
On the basis of anatomical and physiological characteristics, they are classified into 7 classes:
- Mammalia (mammals)
- Aves (birds)
- Reptilia (reptiles)
- Amphibia (amphibians)
- Agnatha (jawless fish)
- Osteichthyes (bony fish)
- Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish)
Mammalia
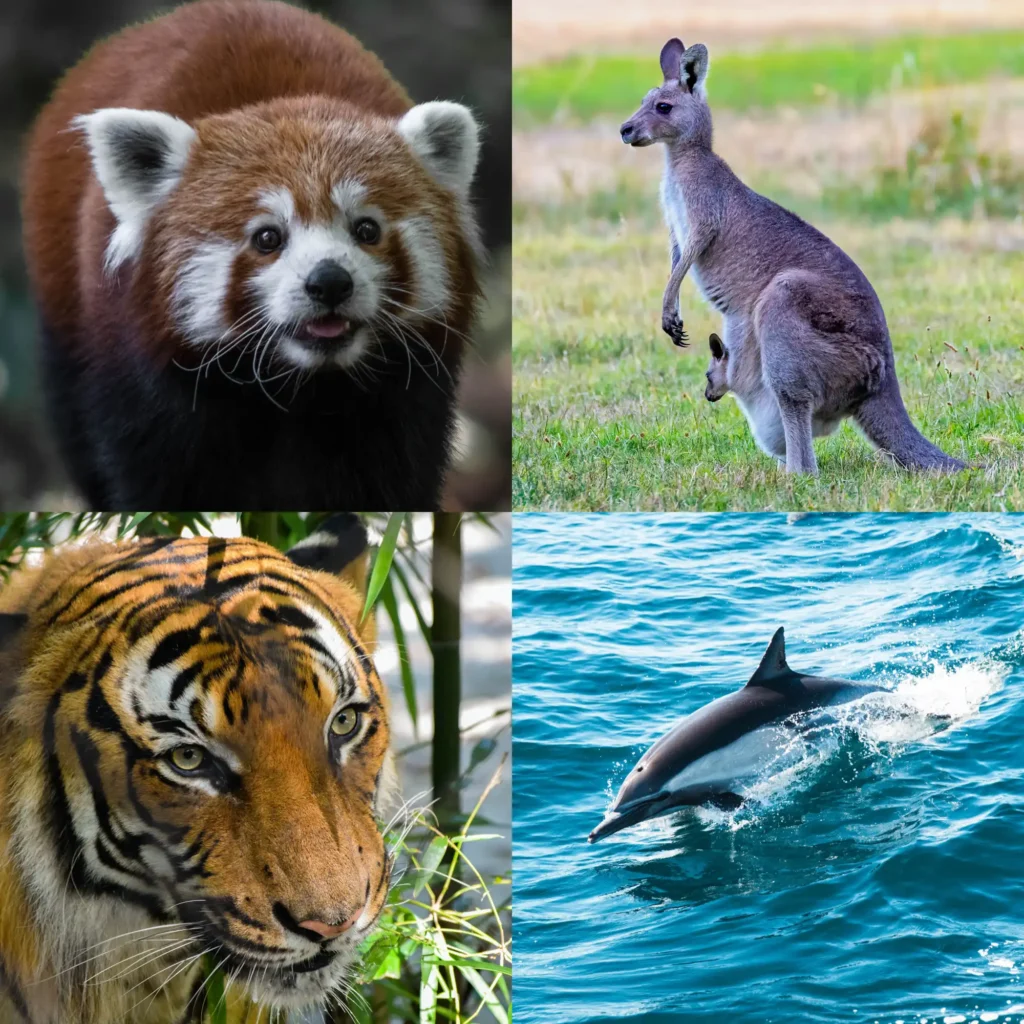

Warm-blooded animals comprise the class of mammals that includes humans. They are vertebrates and have hair. Mammals are the only animal species whose females produce milk to feed their young. All animals, with the exception of platypus and echidna, which lay eggs, give birth to living children. Mammals that fly are called bats.
Aves

Feathers on vertebrates have evolved to allow for active metabolism and flight. They also deposit amniotic fluid. Animals with warm bodies and warm blood types belong to the Aves class.
Reptilia
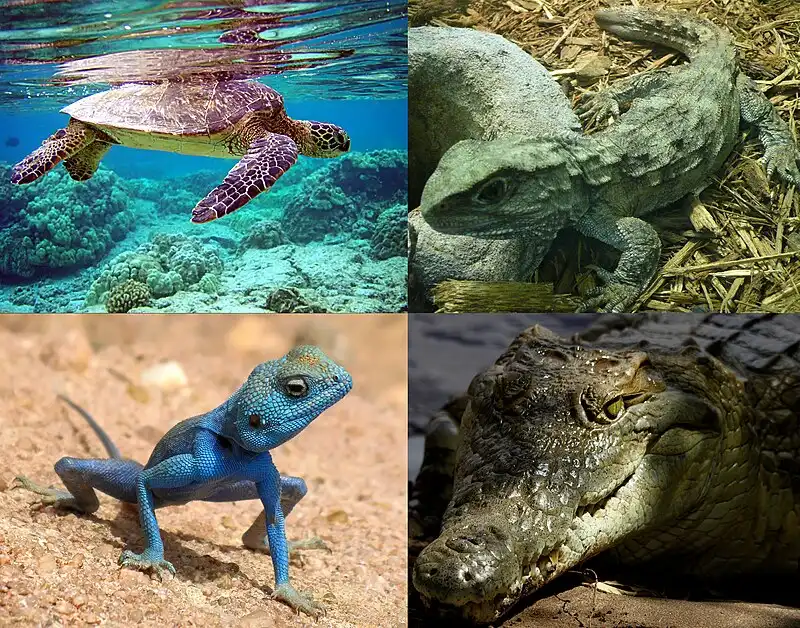

Four-footed tetrapods, reptiles have a tail, cloaca, and a single external nasal entrance. They also lay eggs. Reptiles have characteristics such as internal fertilization, amniotic development, and epidermal scales covering some or all of the body.
Amphibia
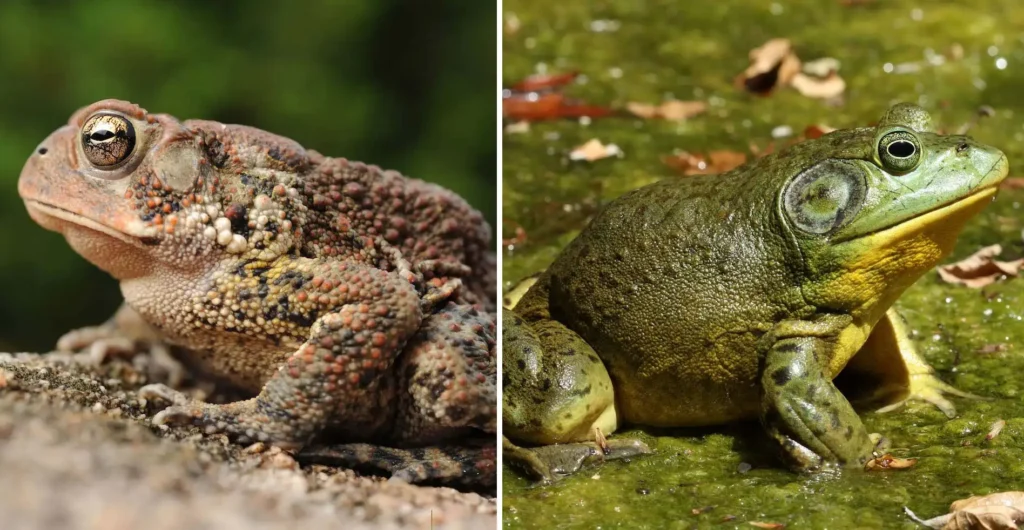

Amphibians are small vertebrates that need water to survive and thrive in humid environments. The members of this class of vertebrates are salamanders, newts, toads, and frogs. They can all breathe and absorb water thanks to their incredibly thin skin. Moreover, amphibians have distinct skin glands that produce protein.
Agnatha
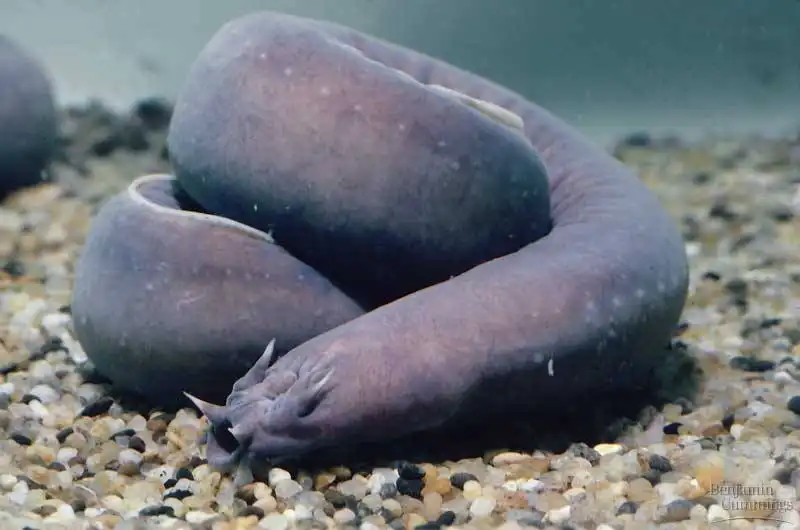

Primitive species of fish without jaws hunt for food or live as parasites. They can only use their circular mouth to suck or rasp, despite lacking an upper and lower jaw. Agnatha fish have highly developed senses of touch and smell, but they have poor vision. Freshwater and saltwater both have easy access to them.
Osteichthyes
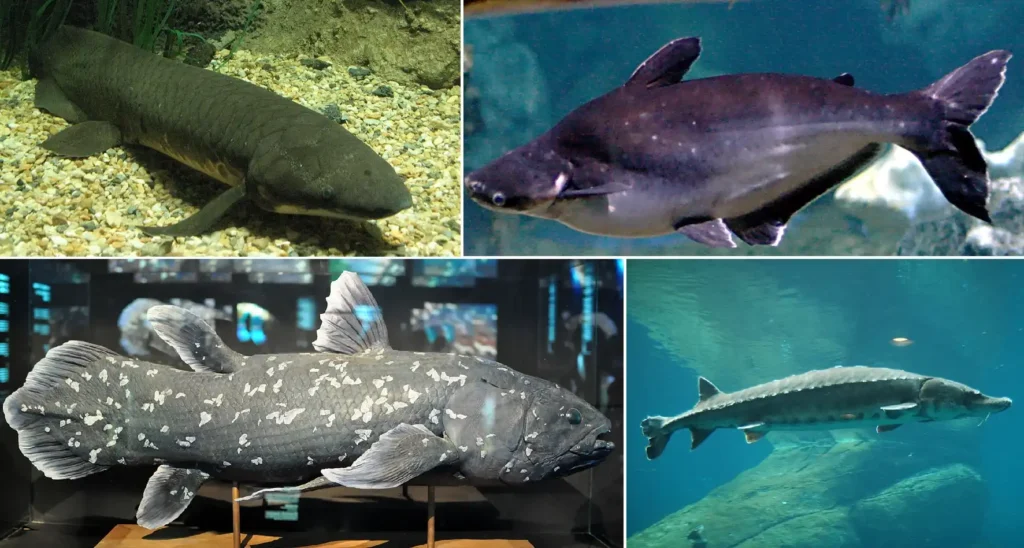

Non-cartilaginous bones are found in the largest class of vertebrates, the cold-blooded Osteichthyes or bony fish. Bony fish have an upper and lower jaw, multiple mucous glands on their skin, fins, five pairs of gills, and, in certain species, a swim bladder to help with balance. These fish are typically taller than wide, and they can live in both freshwater and saltwater. They have an amazing egg-laying capacity.
Chondrichthyes
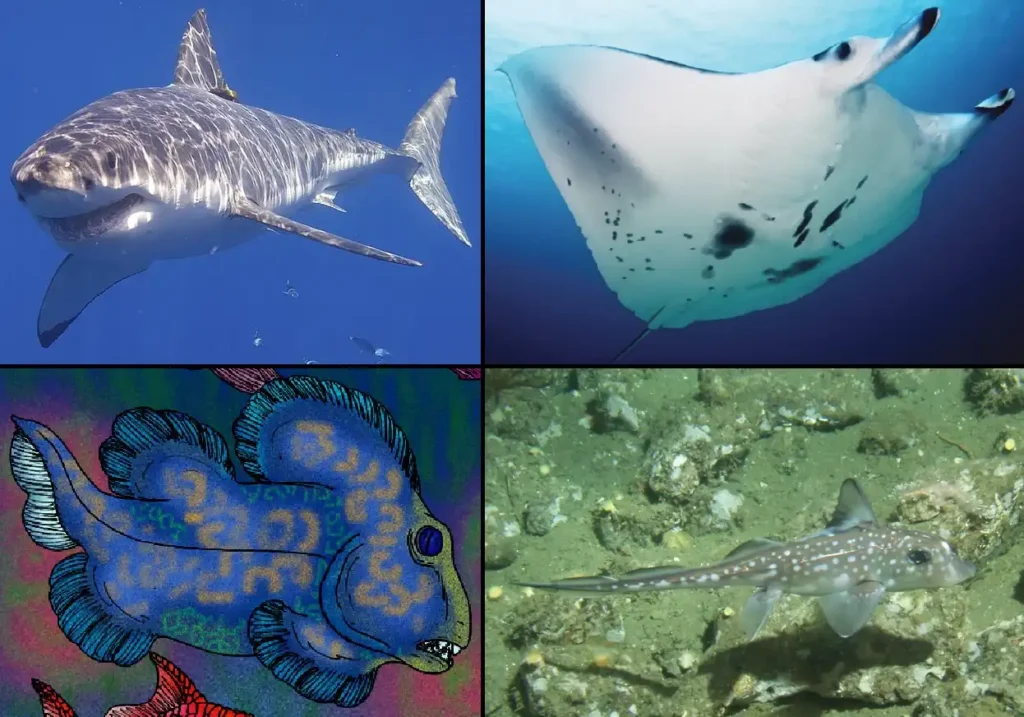

Although the skeletons of cartilaginous fishes are made of cartilage, they nevertheless have paired fins, upper and lower jaws, and scales. Without bone, the bone marrow is unable to produce new blood cells. Fish classified as chondrichthyes are typically wider than tall. Their characteristic sandpaper-like skin is caused by dermal denticles, not by individual scales. There are five to seven gills in a species, and some need to move constantly in order to keep the passage of water and oxygen.
Characteristics of Vertebrates
Some of the common characteristic features of Vertebrates are as follows
- They have a vertebral column.
- They have chambered hearts.
- They have a fully developed skeleton.
- They can breathe through the lungs or gills.
- They have well-developed brains, eyes, and mouths.
Summary
A vertebrate is the term used to describe the bony vertebral column, as we have previously discussed. All vertebrate classes have developed brains, internal skeletons to which muscles can attach, two eyes, closed circulatory systems, and muscular mouths. They are divided into seven classes based on anatomical and physiological traits: amphibians (Agnatha), jawless fish (Osteichthyes), birds (Aves), reptiles (Reptilia), mammals (Mammalia), and cartilaginous fish (Cartilaginous fish). We also talked about a few names for vertebrates.
Read also : List of Top 10 Longest Caves in the World